Difference between revisions of "How to Write a Server"
m (Link format cleanup) |
m (Add Category:Minecraft Modern.) |
||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
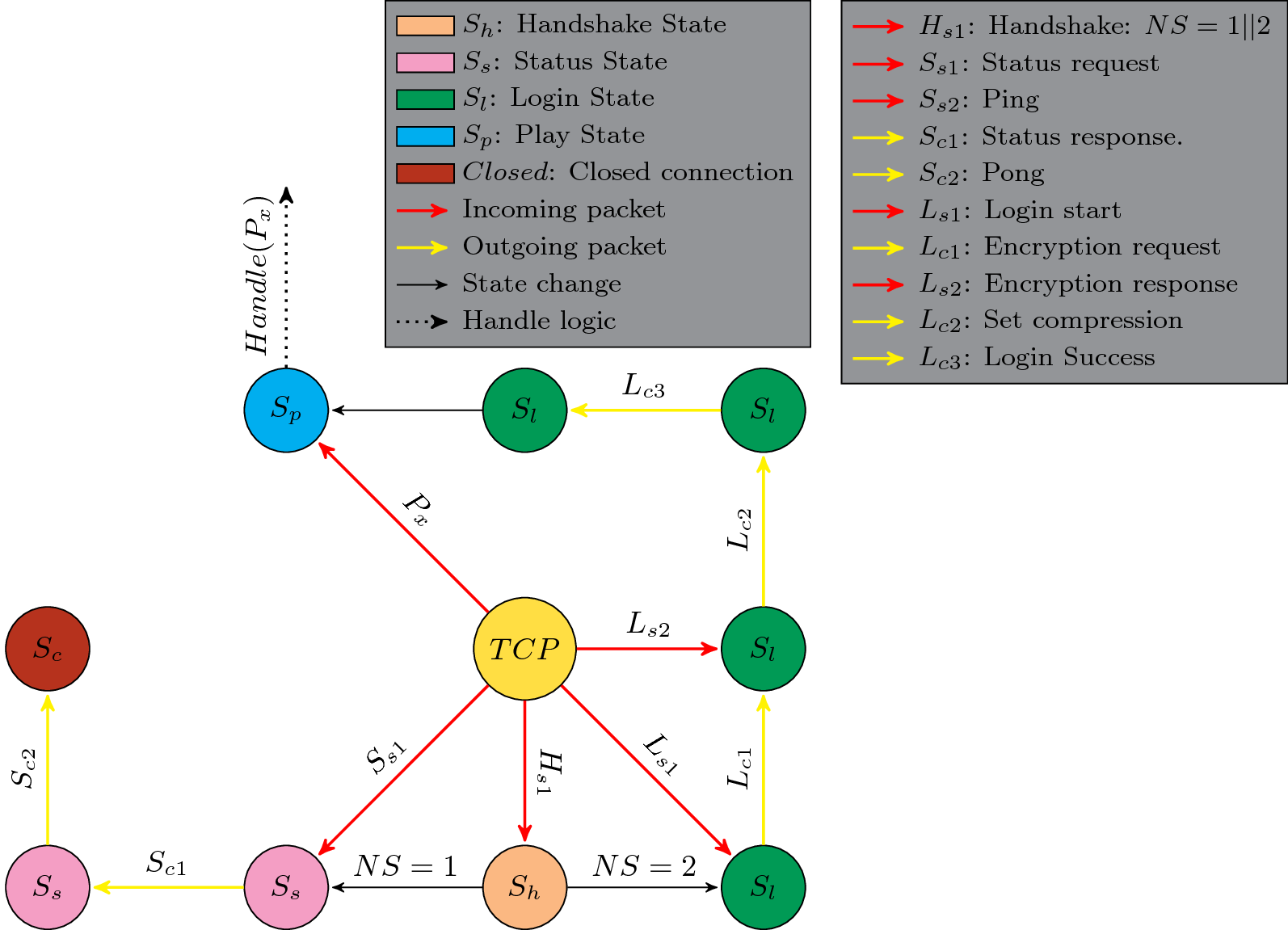
It should be noted that outgoing packets are not directed towards the ''TCP'' node in the middle. This is just because it made a simpler FSM. There is also a possibility to have the [[Protocol#Set_compression|Set compression]] to be sent after [[Protocol#Login_success|Login success]], but it will have a different packet id because the connection state will be [[Protocol#Play|Play]] instead of [[Protocol#Login|Login]]. | It should be noted that outgoing packets are not directed towards the ''TCP'' node in the middle. This is just because it made a simpler FSM. There is also a possibility to have the [[Protocol#Set_compression|Set compression]] to be sent after [[Protocol#Login_success|Login success]], but it will have a different packet id because the connection state will be [[Protocol#Play|Play]] instead of [[Protocol#Login|Login]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Minecraft Modern]] | ||
Revision as of 19:00, 26 February 2024
This tutorial is being created to document what it takes to write a stand-alone server to interact with Notchian clients. The tutorial is incomplete but will be updated whenever more information is discovered.
Contents
Before You Get Started
- Make sure you don't want to fork or join an existing project.
- Wonder why you want to do this in the first place.
- Choose a language that has good networking, like Java, C#, or Python. (If you want to be different, choose a faster language like C or Rust!)
If you're not using a wrapper/library
If you're not using a wrapper/library, then you'll need to do all the dirty work by hand.
Accepting TCP Packets
The Minecraft server accepts connections from TCP clients and communicates with them using packets. A packet is a sequence of bytes sent over the TCP connection. The meaning of a packet depends both on its packet ID and the current state of the connection. The initial state of each connection is Handshaking, and state is switched using the packets Handshake (Handshaking, 0x00, serverbound) and Login Success (Login, 0x02, clientbound). You can read more about Minecraft Packets on the Protocol page.
Server List Ping
Your server needs to accept a Handshake(0x00 with state=1) and a Request packet, which you'll respond with a Response packet including JSON detailing the server. You can read more about this on the Server List Ping page.
FSM example of handling new TCP connections
As an example of how to handle new TCP connections we can have a look at this informal FSM to get an example of how one could write the server's states.
To distinguish between FSM-states and the states of the connection, the different connection states has been colour-coded to make it easier to understand the transitions. The given connection states are:
- Handshake
- Status
- Login
- Play
- Closed (added for clarity, as Pong closed the TCP socket)
It should be noted that outgoing packets are not directed towards the TCP node in the middle. This is just because it made a simpler FSM. There is also a possibility to have the Set compression to be sent after Login success, but it will have a different packet id because the connection state will be Play instead of Login.